WHAT IS ITSM PROCESS?
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses are increasingly reliant on their IT infrastructure to drive operations and deliver exceptional services to customers. To navigate this intricate realm of IT services and resources, organizations turn to IT Service Management (ITSM) processes.
These processes play a pivotal role in optimizing IT service delivery, streamlining operations, and ensuring unparalleled customer satisfaction. This in-depth blog post aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of ITSM processes, covering their significance, key components, benefits, and best practices.
Introduction to ITSM Processes
IT Service Management (ITSM) entails a strategic approach that organizations adopt to design, deliver, manage, and enhance the utilization of IT resources to meet business objectives. At its core, ITSM strives to align IT services with the organization's needs and the expectations of its customers. This alignment and efficient service delivery are achieved through the implementation of ITSM processes.
ITSM processes encompass structured sets of activities that are executed in a coordinated manner to manage IT services across their entire lifecycle. These processes empower organizations to uphold high service quality standards, mitigate downtime, and amplify overall operational efficiency.
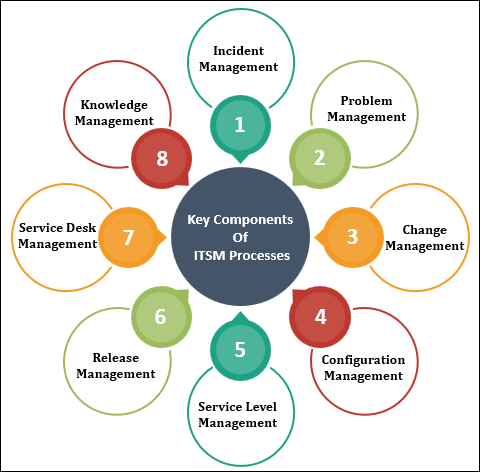
Key Components of ITSM Processes
IT Service Management (ITSM) processes are vital for the effective planning, delivery, and management of IT services within an organization. These processes are a set of interconnected activities that work together to ensure that IT services align with business goals and customer needs. Here are the key components of ITSM processes:
- Incident Management: Incident management focuses on quickly restoring normal service operations after an unexpected disruption. This involves logging incidents, categorizing their impact and urgency, prioritizing them, and resolving them as efficiently as possible.
- Problem Management: Problem management is concerned with identifying and addressing the root causes of recurring incidents. By investigating the underlying issues, organizations can prevent future disruptions and improve service reliability.
- Change Management: Change management ensures that changes to IT services, whether they are software updates, hardware replacements, or process modifications, are planned, approved, and executed in a controlled manner. This minimizes the risk of service disruptions.
- Configuration Management: Configuration management involves maintaining an accurate and up-to-date record of all IT assets, their attributes, and their relationships. This helps in understanding the IT environment, assessing the impact of changes, and managing assets effectively.
- Service Level Management: Service level management focuses on defining, negotiating, and monitoring service level agreements (SLAs) between IT and its customers. SLAs outline the level of service that can be expected and help in measuring service performance.
- Release Management: Release management is responsible for planning, scheduling, and overseeing the rollout of new software releases or hardware changes into the production environment. It ensures that changes are deployed smoothly and without disruptions.
- Service Desk Management: The service desk serves as the primary point of contact between users and IT support. It manages incidents, service requests, and user inquiries, providing timely assistance and facilitating effective communication.
- Knowledge Management: Knowledge management involves capturing, organizing, and sharing valuable information and best practices related to IT services. This knowledge base assists IT teams in faster problem resolution and empowers users to find solutions independently.
Benefits of ITSM Processes
Implementing effective IT Service Management (ITSM) processes can yield a multitude of benefits for organizations of all sizes and industries. These benefits contribute to enhanced service quality, streamlined operations, and improved overall efficiency. Here are the significant advantages of implementing ITSM processes:
- Enhanced Service Quality: ITSM processes prioritize aligning IT services with business goals and customer needs. This alignment results in higher service quality, as IT services are designed and delivered to meet specific requirements, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
- Minimized Downtime: Incident and problem management processes work cohesively to swiftly address disruptions and identify their root causes. This proactive approach reduces downtime by minimizing service interruptions and ensuring rapid incident resolution.
- Efficient Change Management: Properly implemented change management processes help organizations avoid haphazard changes that can disrupt services. Changes are planned, documented, and approved, leading to reduced risks and better stability.
- Optimized Resource Allocation: Configuration and asset management processes enable organizations to efficiently manage their IT resources. This optimization leads to reduced waste, improved resource utilization, and cost savings.
- Faster Problem Resolution: ITSM processes, particularly those focused on knowledge management, provide a repository of solutions and best practices. This speeds up problem resolution as IT teams can access historical data and documented solutions.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many industries are subject to regulations and compliance standards. ITSM processes ensure that services adhere to these standards through rigorous documentation, controls, and auditing practices.
- Improved Communication: Service desk management processes enhance communication between IT teams and end-users. Clear communication channels facilitate faster issue resolution, reduce misunderstandings, and enhance user satisfaction.
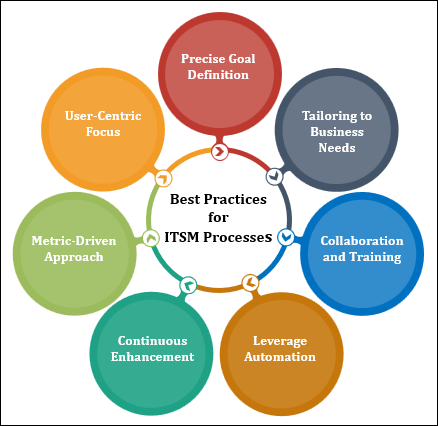
Best Practices for Implementing ITSM Processes
The implementation of ITSM processes demands meticulous planning and execution. Here are paramount best practices to consider:
- Precise Goal Definition: Articulate the goals and objectives underpinning the implementation of ITSM. Whether it's expediting incident response or enriching customer satisfaction, well-defined objectives are the cornerstone.
- Tailoring to Business Needs: Customize ITSM processes to harmonize with the distinct requirements of your organization. Embrace the fact that one-size-fits-all solutions rarely encompass the diverse needs of businesses.
- Collaboration and Training: Engage all pertinent teams and personnel in the design and execution of processes. Comprehensive training ensures that everyone comprehends their roles and responsibilities.
- Leverage Automation: Harness the power of automation tools to streamline repetitive tasks such as incident logging and rudimentary troubleshooting. Automation enhances efficiency and mitigates human error.
- Continuous Enhancement: ITSM processes are dynamic by nature. Regularly assess and refine your processes to assimilate acquired insights and accommodate shifts in technology and business prerequisites.
- Metric-Driven Approach: Envisage key performance indicators (KPIs) to gauge the effectiveness of your ITSM processes. Consistent monitoring of these metrics facilitates tracking progress and identifying avenues for improvement.
- User-Centric Focus: Root the design of ITSM processes in the needs of end-users. Ultimately, the aim is to enhance their experience and satisfaction.
Conclusion
In the ever-changing landscape of IT services, adept ITSM processes serve as the backbone of service quality maintenance, disruption minimization, and operational excellence. Through the implementation of finely tuned and tailored ITSM processes, organizations can augment their capacity to cater to customer needs, propel business expansion, and sustain competitiveness in the technology-driven era. By amalgamating deliberate planning, unceasing improvement, and an unwavering commitment to user contentment, ITSM processes transform into the bedrock of triumphant IT service delivery.








